De 4 C'er | The 4 C's
Diamant (græsk: adámās, dansk: ~ ubetvingelig) er et gennemsigtigt mineral bestående af kulstof. Diamant er det hårdeste kendte mineral (10 på Mohs' hårdhedsskala) og kan derfor kun slibes med støv fra andre diamanter.
Diamanter er dannet i 140-190 kilometers dybde under et enormt tryk og er gennem diatremer (kraterrør) blevet ført op til jordskorpen. Diamanterne findes i bjergarten kimberlit.
En stor del af verdens diamanter kommer fra Sydafrika, Congo, Sibirien, Indien og Brasilien.
En brillant er en rundsleben diamant med et stort antal facetter. Diamanter brænder ved temperaturer over 710°C i en iltrig atmosfære.
Husk at sikre dig, at dit valg af diamant stemmer overens med de 4 C'er, der benyttes til at bedømme kvaliteten og størrelsen på én diamant.
De 4 C'er står for clarity, color, carat og cut:
Clarity - Klarheden på diamanten. Diamanter har oftest indeslutninger/små fejl, der findes helt naturligt i stenen. Fejlfrie diamanter "Flawless" er sjældne og jo færre indeslutninger diamanten har - desto mere værdifuld er den. Der er oftest en del økonomi i at vælge en diamant med små fejl - så længe disse ikke kan ses med det blotte øje. Hovedreglen er, at klarheder fra "FL" (fejlfrie) til "SI1" (små indeslutninger) ikke må have fejl, der kan ses med det blotte øje, men kun under 10 x forstørrelse. Kigger man derimod på diamanter som ren investering - er det ofte de fejlfrie diamanter, som investorer og eksperter opkøber.
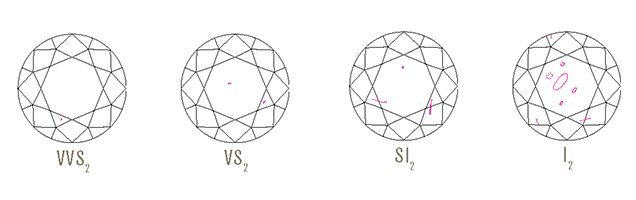
- Flawless (FL) - No inclusions or blemishes are visible to a skilled grader using 10× magnification
- Internally Flawless (IF) - No inclusions and only blemishes are visible to a skilled grader using 10× magnification
- Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2) - Inclusions are difficult for a skilled grader to see under 10× magnification
- Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2) - Inclusions are minor and range from difficult to somewhat easy for a skilled grader to see under 10x magnification
- Slightly Included (SI1 and SI2) - Inclusions are noticeable to a skilled grader under 10x magnification
- Included (I1, I2, and I3) - Inclusions are obvious under 10× magnification and may affect transparency and brilliance
Color - Farven på diamanten. Desto hvidere diamanten er, desto mere værdifuld og sjælden er den. Hvide diamanter kaldes "River" (D-E), "Top Wesselton" (F-G) eller "Wesselton" (H). Gule og sorte diamanter er billigere, da disse forekommer i langt højere grad end de helt hvide. "Fancy" farver, som eksempelvis pink eller blålige, er som hovedregel de dyreste, og her findes der sjældent nye forekomster i minerne.

Carat - vægten på diamanten og dermed størrelsen. 1 carat svarer til 0,2 gram. Større diamanter er selvsagt mere værdifulde end små diamanter - så længe de 3 andre C'er er ens. Her ses hvorledes stigningen i carat, giver en større millimeter på diamanten.

Cut - Slibningen af en diamant. Det helt rigtige slib sikrer, at lyset reflekteres optimalt, hvilket giver diamanten mest spil og liv. Man kan kun slibe diamanter med diamantstøv, da diamanter er det hårdeste mineral man kender. Der bruges oftest komplicerede formler og programmer til at vurdere potentialet af en rådiamant, inden den slibes til én eller flere mindre diamanter.
Det runde brilliantslib er det mest anvendte, men der findes mange alternative slib, der kan differentiere ens smykke fra mængden. Her ses de forskellige slib:
Certifikater - Der findes flere forskellige certifikattyper, når diamanter evalueres. Vi benytter hovedsageligt følgende institutter:
- GIA - Gemological Institute of America
- DGI - Diamond Gemological Institute
- IGI - International Gemological Institute
Certifikater på diamanter er et bevis på, at en uafhængig institution har undersøgt og vurderet kvaliteten. ToftJessens løse diamanter kommer altid med et certifikat, og du kan som kunde søge direkte på det certifikat, som du ønsker. GIA instituttet er kendt som udsteder af det mest kritiske certifikat (GIA), hvor diamanterne vurderes hårdere end eksempelvis certifikater fra DGI eller IGI, med hensyn til de 4 C'er. Derfor er diamanter med certifikat fra GIA oftest dyrere.
Vi vil meget gerne hjælpe med at finde den helt rigtige diamant til dig. Kontakt os gerne med spørgsmål eller forespørgsler.
Se alle vores diamanter | Se alle vores diamantsmykker
[lang2]
Diamond Color Actually Means Lack of Color
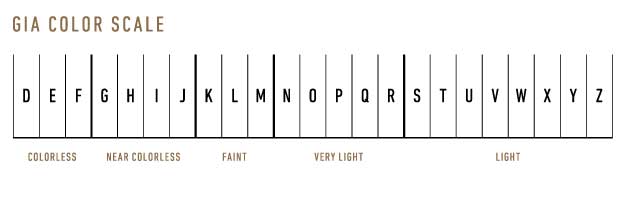
The diamond color evaluation of most gem-quality diamonds is based on the absence of color. A chemically pure and structurally perfect diamond has no hue, like a drop of pure water, and consequently, a higher value. GIA's D-to-Z diamond color-grading system measures the degree of colorlessness by comparing a stone under controlled lighting and precise viewing conditions to masterstones stones of established color value.
GIA's diamond D-to-Z color-grading scale is the industry's most widely accepted grading system. The scale begins with the letter D, representing colorless, and continues, with increasing presence of color, to the letter Z.
Many of these color distinctions are so subtle that they are invisible to the untrained eye; however, these distinctions make a very big difference in diamond quality and price.
Diamond Clarity Refers to the Absence of Inclusions and Blemishes
Natural diamonds are the result of carbon exposed to tremendous heat and pressure deep in the earth. This process can result in a variety of internal characteristics called 'inclusions' and external characteristics called 'blemishes.'
Evaluating diamond clarity involves determining the number, size, relief, nature, and position of these characteristics, as well as how these affect the overall appearance of the stone. While no diamond is perfectly pure, the closer it comes, the higher its value.
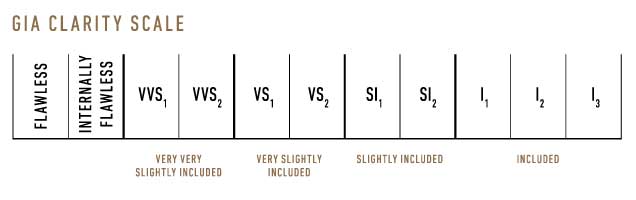
The GIA Diamond Clarity Scale has 6 categories, some of which are divided, for a total of 11 specific grades.
Flawless (FL)
No inclusions and no blemishes visible under 10x magnification
Internally Flawless (IF)
No inclusions visible under 10x magnification
Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2)
Inclusions so slight they are difficult for a skilled grader to see under 10x magnification
Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2)
Inclusions are observed with effort under 10x magnification, but can be characterized as minor
Slightly Included (SI1 and SI2)
Inclusions are noticeable under 10x magnification
Included (I1, I2, and I3)
Inclusions are obvious under 10x magnification which may affect transparency and brilliance
Many inclusions and blemishes are too small to be seen by anyone other than a trained diamond grader. To the naked eye, a VS1 and an SI2 diamond may look exactly the same, but these diamonds are quite different in terms of overall quality. This is why expert and accurate assessment of diamond clarity is extremely important.
A Diamond's Cut Unleashes Its Light
Diamonds are renowned for their ability to transmit light and sparkle so intensely. We often think of a diamond's cut as shape (round, emerald, pear), but a diamond's cut grade is really about how well a diamond's facets interact with light.
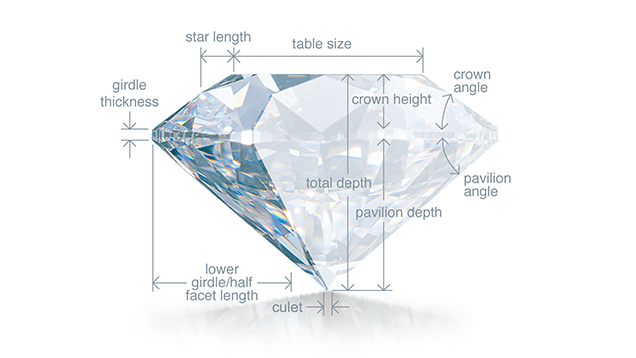
Precise artistry and workmanship are required to fashion a stone so its proportions, symmetry, and polish deliver the magnificent return of light only possible in a diamond.
A diamond's cut is crucial to the stone's final beauty and value. And of all the diamond's 4Cs, it is the most complex and technically difficult to analyze.
To determine the cut grade of the standard round brilliant diamond - the shape that dominates the majority of diamond jewelry – GIA calculates the proportions of those facets that influence the diamond's face-up appearance. These proportions allow GIA to evaluate how successfully a diamond interacts with light to create desirable visual effects such as:
Brightness: Internal and external white light reflected from a diamond.
Fire: The scattering of white light into all the colors of the rainbow.
Scintillation: The amount of sparkle a diamond produces, and the pattern of light and dark areas caused by reflections within the diamond.
GIA's diamond cut grade also takes into account the design and craftsmanship of the diamond, including its weight relative to its diameter, its girdle thickness (which affects its durability), the symmetry of its facet arrangement, and the quality of polish on those facets.
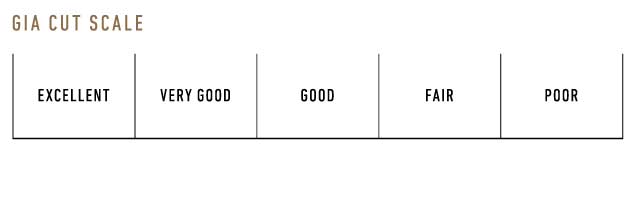
The GIA Diamond Cut Scale for standard round brilliant diamonds in the D-to-Z diamond color range contains 5 grades ranging from Excellent to Poor.
Diamond Carat Weight
Diamond carat weight is the measurement of how much a diamond weighs. A metric "carat" is defined as 200 milligrams.
Each carat can be subdivided into 100 'points'. This allows very precise measurements to the hundredth decimal place. A jeweler may describe the weight of a diamond below one carat by its 'points' alone. For instance, the jeweler may refer to a diamond that weighs 0.25 carats as a 'twenty-five pointer'. Diamond weights greater than one carat are expressed in carats and decimals. A 1.08 carat stone would be described as 'one point oh eight carats.'
All else being equal, diamond price increases with diamond carat weight, because larger diamonds are more rare and more desirable. But two diamonds of equal carat weight can have very different values (and prices) depending on three other factors of the diamond 4Cs: Clarity, Color, Cut, and Carat.
It's important to remember that a diamond's value is determined using all of the 4Cs, not just carat weight.
Source: GIA